5 REASONS
WHY
You should ask your doctor about a low-dose birth control pill
FOR PREGNANCY PREVENTION∗
Hormones play a big role in your menstrual cycle and your ability to get pregnant, so it makes sense that they play a role in pregnancy prevention.
Before you dive in,
*If you are moderately obese, discuss with your healthcare provider whether Lo Loestrin ® Fe is appropriate for you.
*If you are moderately obese, discuss with your healthcare provider whether Lo Loestrin Fe is appropriate for you.
HOW BIRTH CONTROL PILLS WORK
Birth control pills are a type of oral contraceptive that use hormones, similar to the ones in your body, to keep the ovaries from releasing an egg. Without an egg, sperm have nothing to fertilize—so no pregnancy.
A survey of more than 1,000 U.S. women aged 18–45 that included current and
potential birth control pill users found:
.png)
78% of women worry about the amount of hormones they are exposed to through the use of pills†
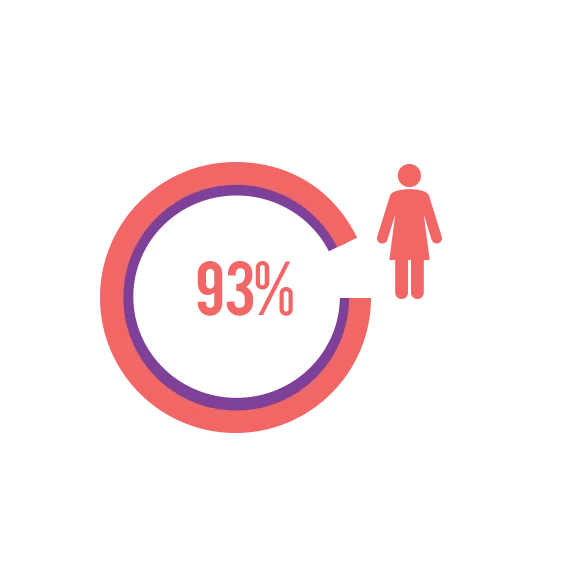
93% are interested in a pill with the lowest amount of daily estrogen‡
Source: Online survey conducted by the Harris Poll on behalf of AbbVie, between July 7–14, 2014, among 1005 U.S. women aged 18-45 currently
using oral contraceptives (OCs) or considering use in the next 6 months.
†Survey respondents could choose from the following to indicate their level of worry about the amount of hormones they are exposed to through the use of OCs: extremely worried, very worried, somewhat worried, and not at all worried. The 78% value represents those who answered extremely worried, very worried, and somewhat worried.
‡Survey respondents could choose from the following to indicate their interest in an OC with the lowest amount of daily estrogen: extremely
interested, very interested, somewhat interested, and not at all interested. The 93% value represents those who answered extremely interested, very interested, and somewhat interested.

You should ask your doctor about a low-dose birth control pill
So, you’re sitting at home thinking to yourself, “Should I talk to my doctor about a low-dose birth control pill like Lo Loestrin® Fe for pregnancy prevention?”
OBVI. But really. Need 1 reason?
How about 5?

.png)
Low-dose oral contraceptives (OCs) can help get the job done.
Lo Lo has the lowest daily dose of estrogen available among birth control pills at just 10 mcg daily. Low estrogen. Effective birth control when taken as directed. Good to know!
2
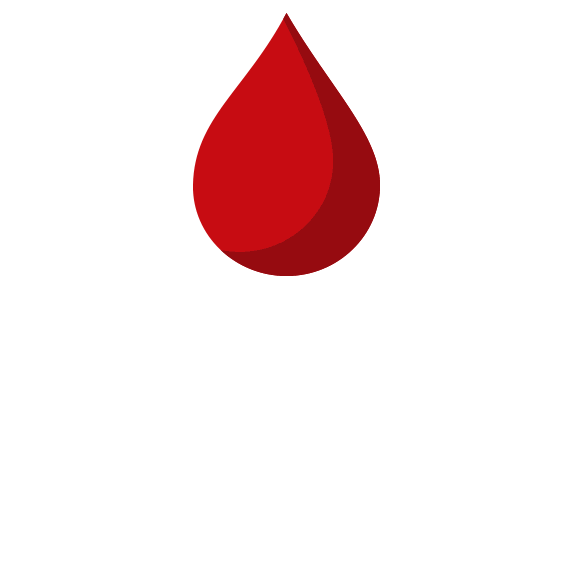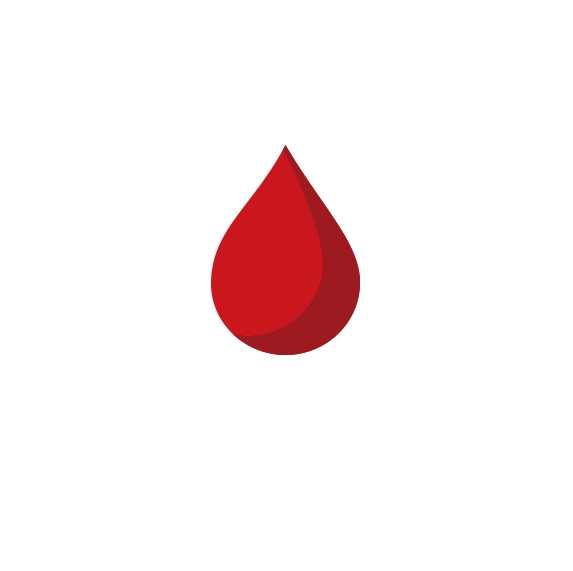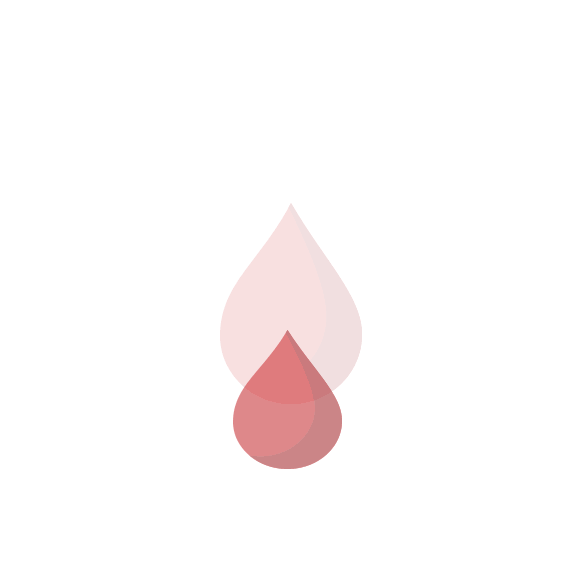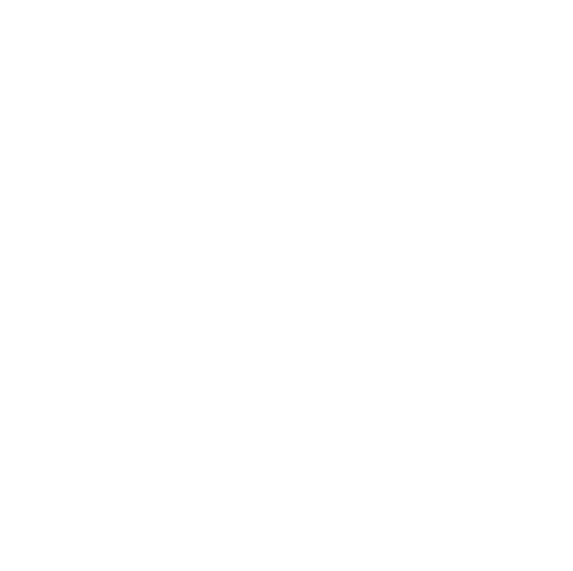
Low-dose birth control pills offer pregnancy prevention that may also result in
short, lighter periods.
4
1
Most women can take a birth control pill for as long as they want during their reproductive lives. So basically, a pill a day and effective pregnancy prevention? Yes please.
3
Low-dose birth control pills make up 45% of the U.S. market.
Lo Loestrin Fe is the #1-prescribed branded birth control pill by OB/GYNs.1

5
And last but not least, you know what’s in pretty much everything you put in your body, but you don’t know how much estrogen is in your birth control pill? It’s time to change that!
So, what are you waiting for? Ask your doctor about Lo Loestrin Fe for pregnancy prevention.
MYTHS ABOUT THE PILL
There are many different types of hormonal birth control pills. They vary based on formula and composition. Your healthcare provider can help determine the right one for you that fits your unique needs and lifestyle.
The birth control pill should be taken at the same time every day to prevent pregnancy. Of course, you can stop taking the pill whenever you wish, especially if you want to become pregnant. It’s always a good idea to visit your healthcare provider for a pre-pregnancy checkup before you stop taking the pill.
While some women may believe that they need to take “a break” from the pill once in a while, you should talk to your healthcare provider to learn more and to understand what’s appropriate for you based on your individual medical needs.
Keep in mind, taking a break from the pill increases your risk of an unwanted pregnancy, so it’s a good idea to use another method of birth control if you don’t want to get pregnant.
What is Lo Loestrin® Fe?
Lo Loestrin Fe is a prescription birth control pill used for the prevention of pregnancy. If you are moderately obese, discuss with your healthcare provider whether Lo Loestrin Fe is appropriate for you.
Do not use Lo Loestrin Fe if you smoke cigarettes and are over 35 years old. Smoking increases your risk of serious cardiovascular side effects (heart and blood vessel problems) from birth control pills, including death from heart attack, blood clots, or stroke. This risk increases with age and the number of cigarettes you smoke.
Who should not take Lo Loestrin Fe?
Do not use Lo Loestrin Fe if you have or have had blood clots, history of heart attack or stroke, high blood pressure that medicine cannot control, breast cancer, liver disease or liver tumors, unexplained bleeding from the vagina, or if you take Hepatitis C drugs containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, as this may increase levels of liver enzymes in the blood.
What else should I know about taking Lo Loestrin Fe?
Treatment with Lo Loestrin Fe should be stopped if you have a blood clot, and at least 4 weeks before and through 2 weeks after major surgery. You should not take Lo Loestrin Fe any earlier than 4 weeks after having a baby, or if you are breastfeeding. If you experience yellowing of the skin or eyes due to problems with your liver, you should stop taking Lo Loestrin Fe. If you are prediabetic or diabetic, your doctor should monitor you while using Lo Loestrin Fe. Your doctor should evaluate you if you have any significant change in headaches or irregular menstrual bleeding. Lo Loestrin Fe should not be taken during pregnancy.
What are the most serious risks of taking Lo Loestrin Fe?
Lo Loestrin Fe increases the risk of serious conditions including blood clots, stroke, and heart attack. These can be life-threatening or lead to permanent disability.
What are the possible side effects of Lo Loestrin Fe?
The most common side effects reported by women taking Lo Loestrin Fe in a study were nausea/vomiting, headache, spotting or bleeding between menstrual periods, painful menstruation, weight change, breast tenderness, acne, abdominal pain, anxiety, and depression.
Birth control pills do not protect you against any sexually transmitted disease, including HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call
1-800-FDA-1088.
US-LOL-230016
Please see the full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning, and Patient Information.
REFERENCES
1. Data on File, AbbVie Inc. IQVIA NPA Audit February 2023. 2. Data on File, AbbVie Inc. IQVIA Patient Insights (NBRx) Audit January 2023.